Tylenol, Leucovorin, and Child Neurodevelopment
Just the proven biochemical, pharmacologic, and clinical facts, Ma’am.
| ROBERT W MALONE MD, MS SEP 25 |
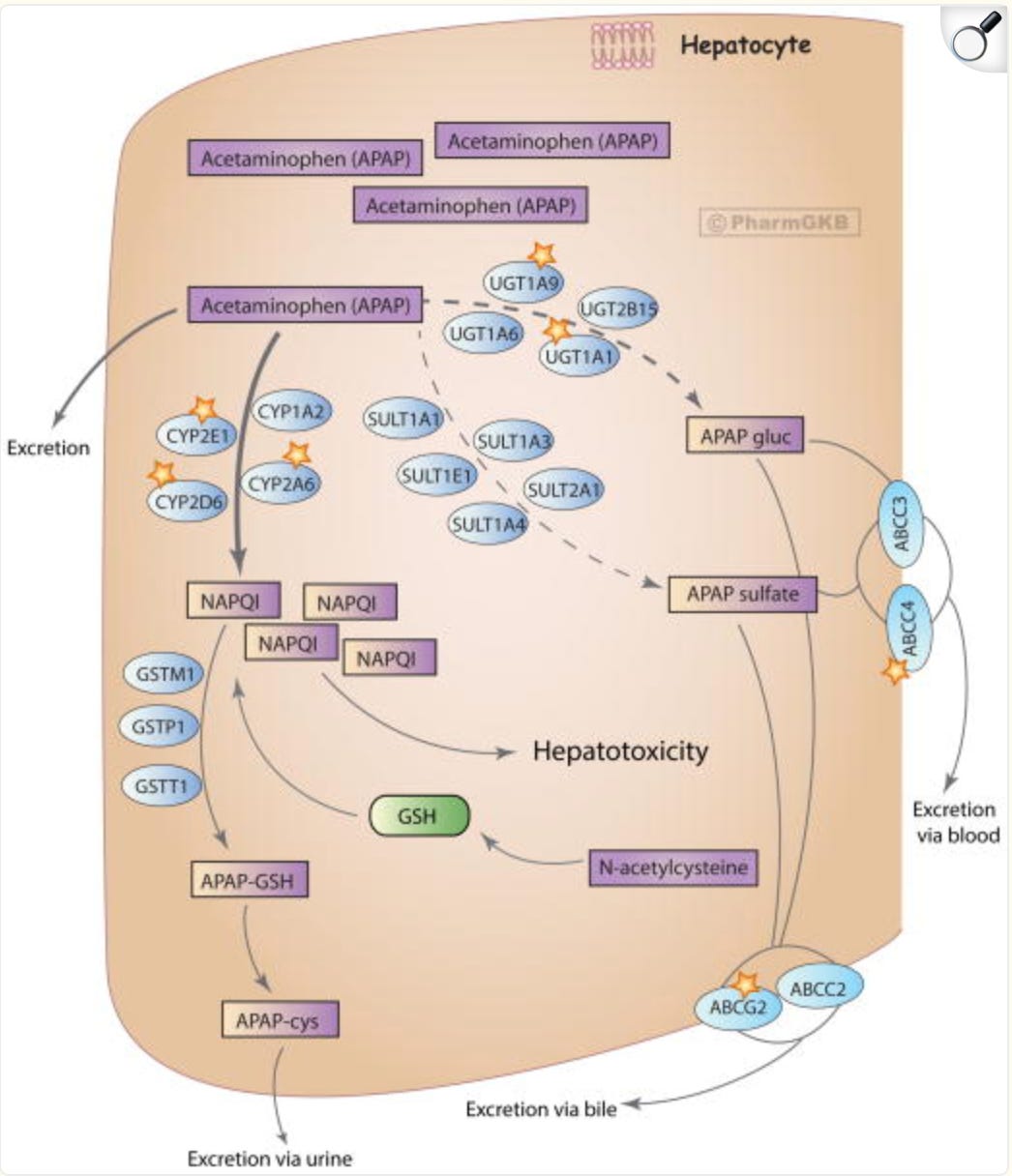
Metabolism and transport of acetaminophen in the liver at highly toxic doses.
Figure 2, from “PharmGKB summary: Pathways of acetaminophen metabolism at the therapeutic versus toxic doses”
Here we go again. Even former President Obama is jumping into the Tylenol/Acetaminophen controversy. Everyone is suddenly an expert, and every statement about public health must be politically weaponized. Suppose you had any doubt that Trump Derangement Syndrome is a real thing. In that case, all you need to do is watch the Instagram reels of left-wing pregnant women downing large doses of Tylenol, which is a high-speed route to the emergency room promptly followed by a potential rather unpleasant death from liver failure. Quod erat demonstrandum (QED).
And by the way, even way back in the day when I was an MD/PhD (Medical Research Scholar Training Program) student at Northwestern University in Chicago, we were taught to be on the lookout for suicide by Tylenol overdose. Whatever you may think of Northwestern U (now rather woke…), it was ranked in the top tier of US Medical Schools at the time, primarily due to its exceptional clinical training.
Note to those suffering from TDS- do not overdose on Tylenol. Tylenol overdose can kill you. How does it kill? By depleting a key molecule called glutathione, which is involved in the biochemical pathway by which Acetaminophen (eg Tylenol) is metabolized (broken down), which happens primarily in the liver. Like all drugs (and vaccines), Tylenol is toxic when taken in sufficient doses that exceed the “therapeutic window”.
The only question is whether or not the FDA has previously defined that “therapeutic window” too broadly. And, in the case of the developing brain, data suggest a strong risk that, in fact, the FDA has been too promiscuous in its Tylenol dosing guidance. For the most part, epidemiological analyses suggesting otherwise appear to have been compromised by previously unrecognized and unaccounted-for confounding variables. I am running a few minutes late; my previous meeting is running over.
Sound familiar?
The FDA and US HHS are now moving to correct that longstanding oversight. POTUS, who has a deep, longstanding, 20 year personal interest in Autism and ASD, has announced this shift in FDA policy and guidance in a press conference. And both dead media and their clients have mounted an aggressive campaign to attack and delegitimize the messengers. But unlike propaganda and marketing, data and actual objective clinical/scientific research are stubborn things.
For budding, wannabe or armchair Biochemists and Pharmacologists, here are the gory details:
Acetaminophen metabolism occurs primarily in the liver through three main pathways: glucuronidation (accounting for 45-55% of metabolism), sulfation (30-35%), and cytochrome P450-mediated oxidation, mainly by CYP2E1, which produces the highly reactive toxic intermediate N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). At therapeutic doses, NAPQI is rapidly detoxified by conjugation with glutathione (GSH), forming non-toxic metabolites excreted in the urine. However, during overdose, the glucuronidation and sulfation pathways become saturated, leading to increased oxidation and NAPQI formation, which depletes hepatic GSH stores; unbound NAPQI then covalently binds to cellular proteins, causing oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and hepatocyte necrosis.
For further details, see “PharmGKB summary: Pathways of acetaminophen metabolism at the therapeutic versus toxic doses”.
Metabolism and transport of acetaminophen in the liver at highly toxic doses. After ingestion of highly toxic doses of acetaminophen, glucuronidation and sulfation pathways get saturated and higher portion of the drug gets oxidized and excreted unchanged. Excess NAPQI depletes glutathione stores causing liver injury. Administration of NAC provides an exogenous source of glutathione that will neutralize NAPQI and prevent further hepatotoxicity. Enzymes playing a major role in the corresponding pathway are denoted with a star. APAP, acetaminophen; APAP gluc, acetaminophen glucuronide; APAP-cys, acetaminophen cysteine; NAPQI, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine; NAC, N-acetylcysteine. A fully interactive version is available online at http://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA166117881.
What is Leucovorin?
What is this drug that the FDA and NIH are endorsing as a potential treatment for some cases of Autism/Autism Spectrum disorder (ASD)? Leucovorin is otherwise known as Folinic acid. It is basically a synthetic vitamin, chemically and pharmacologically related to the vitamin known as Folic acid or B9.
Once again, for budding, wannabe or armchair Biochemists and Pharmacologists, here are the gory details:
Folic acid and folate differ significantly in their chemical structure. Folic acid is the fully oxidized, synthetic form of vitamin B9, existing as a monoglutamate, meaning it contains only one glutamate residue. In contrast, naturally occurring folates in food are predominantly in the reduced form and exist as polyglutamates, containing multiple glutamate residues (typically more than one). The pteridine ring in folic acid is fully oxidized, which contributes to its high stability, whereas natural folates have a reduced pteridine ring that is chemically less stable and more susceptible to degradation by heat, oxidation, and light. Furthermore, folic acid is not found in nature and is not a normal metabolite, while folate is the generic term for a group of compounds with similar nutritional properties, including natural food folates and bioactive reduced forms. The chemical structure of folic acid consists of a pterin ring conjugated to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) by a methylene bridge, which is then linked to a single glutamic acid residue via a peptide bond.
Adequate levels of folate are necessary to support fetal and child neurodevelopment. Administration of Folinic acid to a subset of children with ASD can result is marked improvements in ASD symptoms, including overall cognitive and communication function.
As mentioned, Folinic acid has been clinically observed to provide benefits to a subset of patients suffering from ASD.
Here are some references that you (or Dead Media narrative reinforcers masquerading as “reporters” ) might wish to review-
- Efficacy of methylcobalamin and folinic acid treatment on glutathione redox status in children with autism.
James SJ, Melnyk S, Fuchs G, Reid T, Jernigan S, Pavliv O, Hubanks A, Gaylor DW. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Dec 3;89(1):425-30. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26615. PMCID: PMC2647708
Frye RE, Sequeira JM, Quadros EV, James SJ, Rossignol DA. Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Jan 10;18(3):369-81. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.175. PMCID: PMC3578948
- Folinic acid improves verbal communication in children with autism and language impairment: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.
Frye RE, Slattery J, Delhey L, Furgerson B, Strickland T, Tippett M, Sailey A, Wynne R, Rose S, Melnyk S, Jill James S, Sequeira JM, Quadros EV. Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Oct 18;23(2):247-256. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.168. PMCID: PMC5794882
- Efficacy of Folic Acid Supplementation in Autistic Children Participating in Structured Teaching: An Open-Label Trial.
Sun C, Zou M, Zhao D, Xia W, Wu L. Nutrients. 2016 Jun 7;8(6):337. doi: 10.3390/nu8060337. PMCID: PMC4924178
Apparently these findings are supported by expert opinion and research at the NIH. Notice anything about these publications and journals? These findings are not being published in ‘big” journals. Despite the growing incidence and prevalence of ASD, this basic and clinical research area has been treated as if any research or findings relating to ASD diagnosis and treatment are outside the Overton window of allowable medical and scientific discourse.
Why, you ask? Good question. I do not have a good answer. “Ask your doctor”.
How are glutathione and folic acid related to neurodevelopment?
Glutathione and folic acid are both closely tied to neurodevelopment, although through different yet interconnected biochemical pathways. Folic acid fuels the methylation cycle and supplies precursors for glutathione, while glutathione safeguards the developing brain from oxidative stress. Together, they form a biochemical partnership essential for healthy neurodevelopment.
Tylenol depletes the body’s reserves of glutathione by the mechanisms discussed above. At sufficient doses, this can cause death. At sublethal doses in infants and the developing fetus, reduction in available glutathione can result in neurodevelopmental damages.
Commonly recommended prenatal folic acid administration during pregnancy improves outcomes partly because it supports both methylation for neurodevelopment and glutathione production for oxidative balance. Low glutathione levels have been observed in some children with neurodevelopmental disorders, and boosting folate/related nutrients (B12, B6, betaine) can sometimes improve redox balance. There are currently active investigations into whether supporting folate-dependent glutathione pathways can reduce neurodevelopmental risk in susceptible populations.
Folic Acid in Neurodevelopment
- DNA synthesis & repair: Folic acid (vitamin B9) is crucial for one-carbon metabolism, which provides methyl groups needed for DNA synthesis and repair during rapid cell division in the developing brain.
- Neural tube closure: Adequate folate in early pregnancy prevents neural tube defects (like spina bifida and anencephaly). This is why folic acid supplementation is universally recommended before and during pregnancy.
- Methylation & gene regulation: Folate supports S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) production, the body’s main methyl donor, which regulates gene expression via DNA and histone methylation. Epigenetic regulation is vital for brain development and function.
Glutathione in Neurodevelopment
- Master antioxidant: Glutathione protects developing neurons from oxidative stress, which is especially high in the brain due to rapid growth and high oxygen consumption.
- Detoxification: It helps remove reactive oxygen species and toxic byproducts that, if left unchecked, can impair neuronal migration, synapse formation, and myelination.
- Redox regulation: Beyond antioxidant defense, glutathione influences redox signaling that guides normal neuronal differentiation and survival.
The Link Between Folic Acid and Glutathione
- Shared pathway: one-carbon metabolism
- Folate metabolism produces homocysteine. Homocysteine can either be remethylated back to methionine (with folate/B12 help) or enter the transsulfuration pathway, where it ultimately contributes to glutathione synthesis.
- In other words, folate status indirectly determines how much raw material is available for glutathione production.
- Balance of methylation vs. antioxidant defense: The body must allocate one-carbon units between methylation (epigenetics, DNA synthesis) and glutathione (redox protection). Both are critical for neurodevelopment.
- Deficiency links: Low folate can raise homocysteine and impair glutathione synthesis, leading to both oxidative stress and disrupted epigenetic programming—factors implicated in conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, developmental delay, and neural tube defects.
Those are just the facts, Ma’am. And by the way, neither Obama during this three terms as POTUS/shadow POTUS nor his HHS “leadership”, did nothing substantial about autism and ASD, and he has absolutely no medical training. That is also a fact.
Now there is an issue that Dead Media narrative reinforcers SHOULD be looking into.
